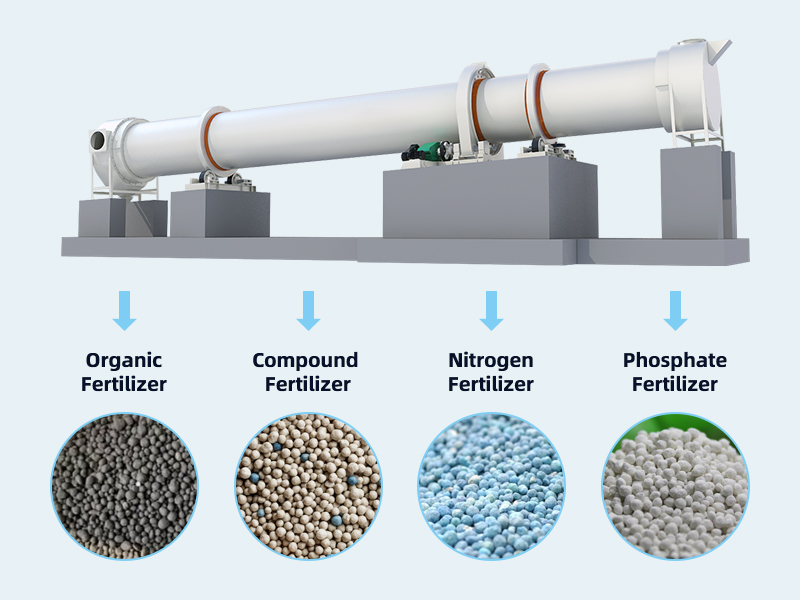
Rotary Drum Dryer: Best Selection of Fertilizer Drying Machine
Why dry fertilizers?
Benefits of drying fertilizers include:
-
Preventing clumping: Wet fertilizer granules have high moisture and are prone to breaking and clumping. Dried fertilizers have lower moisture, making them more durable for storage, and less likely to clump or spoil.
- Extending shelf life: Dried fertilizers are more stable and retain their effectiveness longer.
- Improving efficiency: Dry fertilizers are easier to spread evenly, increasing their efficiency.
- Reducing weight: Drying lowers the moisture content, reducing weight and volume, which cuts transportation costs.
- Secondary granulation: The dryer not only dries but can also perform secondary granulation, improving the solubility of organic fertilizers, increasing granulation rate, ensuring uniform particles, and boosting yield.
Rotary drum dryer: key equipment for fertilizer drying
1. Uniform drying
2. Energy efficiency
3. High throughput
4. Fast drying speed
5. Strong insulation
6. Versatile fuel use
4 key factors in the fertilizer drying process
1. Residence time in the rotary dryer
2. Temperature in the dryer
3. Airflow in the dryer
4. Heat exchange in the dryer
Common problems in fertilizer drying
Problem 1: Excessive large particles or clumps
Reasons Solutions 1. Excess moisture in granulation or high initial moisture Reduce water in granulation or use dewatering equipment 2. Low dryer temperature Increase temperature and check combustion system 3. Uneven screening Add or adjust screening equipment 4. Incorrect rotation speed Adjust to the optimal speed
Problem 2: Excessive fine powder
Reasons Solutions 1. Insufficient liquid phase during granulation Increase steam and moisture in the granulator 2. Low viscosity of compost Adjust formula and increase viscosity additives 3. Excessive drying temperature or time Lower temperature or shorten drying time 4. Uneven mixing of returned and fresh materials Improve mixing equipment or extend mixing time 5. Equipment wear or aging Regularly inspect and maintain equipment, replace worn parts
Statement: If the content on this site infringes upon the legitimate rights and interests of the original author, please contact this site to delete it.

